The 2017 Nobel Prizes were recently awarded in early
October. Annual Nobel Prizes are awarded for achievement in Physics, Chemistry,
Physiology/Medicine, Economics, Literature, and Peace.
Educating the Masses About QUALITY Science...One (Well-Cited) Rant at a Time
Sunday, November 5, 2017
Tuesday, June 27, 2017
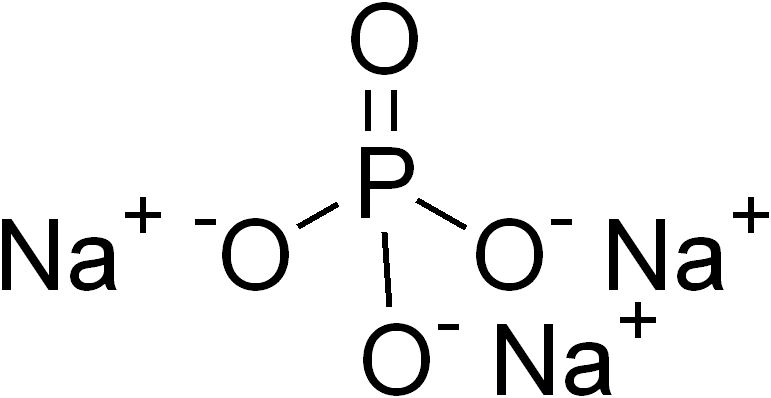
Trisodium Phosphate in Food: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love Paint Thinner
A
recent internet freak-out that may have passed under the radar for many out
there concerns the presence of a potentially toxic food additive in cereal that
is also found in paint thinner and cleaning agents.
The ingredient in question is Trisodium Phosphate (TSP), a salt compound with many diverse uses including paint
thinning, cleaning, other degreasing, and removing oxidized metal for
soldering. Interestingly, and the source of controversy, TSP is also used as a
food additive and a nutritional supplement for exercise.
While this conspiracy theory originally dates back to at least 2014, it
has recently made the rounds on social media within the past month.
Despite being thoroughly debunked by Snopes the meme continues. This serves as
just a single example of an ongoing chemophobia – distrust of anything seen as
an unnatural “chemical” – among esteemed internet dietary experts.
Much of TSP’s functionality comes from its strong basicity,
as it has a pH=12 as a 1% solution. Its basic properties will promote reaction
with fatty acids through saponification, breaking
down grease and oil and thus serving as a cleaner and degreaser (or paint
thinner). These functionalities also make it useful as a food additive, as its
saponification ability is useful in cheese sauces and it can prevent
acidification of food. It also prevents moisture buildup and has some
antimicrobial properties. Interestingly, it is also used as an exercise enhancer,
presumably due to the need for phosphates in aerobic metabolism.
While TSP use has dwindled due to phosphates being
recognized as a major contributor to eutrophication
(promoting algae growth in water bodies), it is “Generally Recognized As Safe”
for human consumption by the US Food and Drug Administration. It can be very corrosive at high concentrations due to its
basic properties, however there is no substantial evidence of
long-term effects at low doses for TSP or other phosphates.
It is only natural (get it) to be concerned when a
chemical involved in industrial processes appears in our food. However while in
this case the food additive is in fact the active ingredient in
cleaners/degreasers and not merely an unrelated component, it is the
concentration and context that matter. The basicity and phosphate chemistry of
TSP make it a useful compound for a diverse set of functions, however the
chemical reactions necessary for those functions are restricted by the
specifics of the chemical concentration, media, and form. It is often the
important nuances and details that are left out of a tweet or meme.
Tuesday, February 21, 2017
How Effective is Hand Sanitizer?
There are a few standards that everyone keeps on them in
their bag. Moisturizer, chapstick, and a bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand
sanitizer, with Purell being the eponymous brand name, is available in many
public buildings, and some people use it following every touch of a door
handle. Purell is a watery gel that is rubbed into one’s hands as a sanitizing
agent in lieu of available soap and water. There are different types of hand
sanitizer, but the active ingredient in Purell and many common brands is simply
ethanol, which universally
kills bacteria by dissolving their cell membrane and destroying proteins.
While hand sanitizer is known to be very effective at killing
bacteria, for some people it serves as more of a security blanket in response to
any and all skin contact.
The question is, does the availability of hand
sanitizer provide a false sense of sanitation?
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)